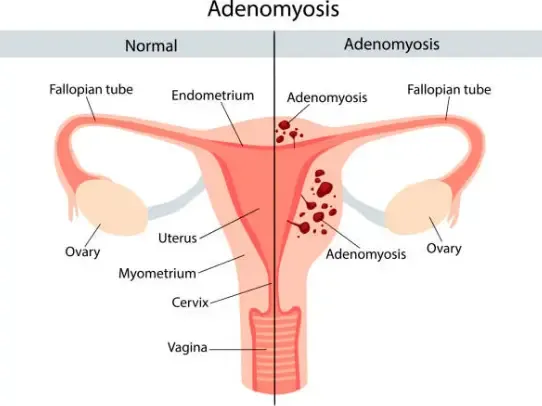
Adenomyosis is a gynecologic condition that affects the uterus, causing the tissue that lines the uterus to grow into the muscular wall. This can result in an enlarged uterus and heavy menstrual bleeding. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for adenomyosis.
What is Adenomyosis?
Adenomyosis occurs when the endometrial tissue, which normally lines the uterus, infiltrates and grows into the muscular walls of the uterus. This misplaced tissue behaves similarly to the uterine lining, thickening and shedding during each menstrual cycle. However, since the tissue is embedded within the uterine muscle, it can lead to various symptoms and complications.
Causes of Adenomyosis
The exact cause of adenomyosis is still unknown, but several theories have been proposed. One theory suggests that invasive tissue growth occurs when endometrial cells invade the uterine muscle, potentially due to uterine incisions made during surgeries like cesarean sections. Another theory suggests that adenomyosis may have developmental origins, with endometrial tissue deposited in the uterine muscle during fetal development. Additionally, postpartum uterine inflammation has been linked to the development of adenomyosis. Lastly, recent research has proposed a connection between adenomyosis and bone marrow stem cells invading the uterine muscle.
Risk Factors for Adenomyosis
Certain factors may increase a woman's risk of developing adenomyosis. These include prior uterine surgeries, such as cesarean sections or dilation and curettage procedures. Childbirth and middle age are also associated with an increased risk of adenomyosis. It is most commonly found in women in their 40s and 50s, although recent studies suggest that it can also affect younger women.
Symptoms of Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis can present with a range of symptoms, although some women may not experience any noticeable signs. Common symptoms include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, severe cramping during menstruation, chronic pelvic pain, painful intercourse, and an enlarged uterus. Some women may also experience tenderness or pressure in the lower abdomen.
Diagnosing Adenomyosis
If you experience prolonged, heavy bleeding or severe menstrual cramping that interferes with your daily activities, it is important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. The diagnosis of adenomyosis typically involves a physical examination and imaging tests. During a physical exam, your doctor may palpate the uterus to check for any abnormalities. Imaging tests such as ultrasounds and MRIs can provide more detailed information about the thickness of the uterine walls and the presence of adenomyosis.
Adenomyosis vs. Endometriosis vs. Uterine Fibroids
Adenomyosis, endometriosis, and uterine fibroids are all conditions that affect the female reproductive system and can cause similar symptoms. However, they are distinct conditions that require different treatment approaches. Adenomyosis specifically involves the growth of endometrial tissue within the uterine walls. Endometriosis, on the other hand, occurs when endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus, potentially affecting other organs. Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that develop within the uterus.
Complications of Adenomyosis
While adenomyosis itself is not harmful, it can lead to complications such as chronic anemia in women who experience prolonged, heavy bleeding during their periods. Chronic anemia can cause fatigue, dizziness, lightheadedness, and shortness of breath. Additionally, the pain and excessive bleeding associated with adenomyosis can significantly impact a woman's quality of life and restrict her daily activities.
Treatment Options for Adenomyosis
The treatment approach for adenomyosis depends on the severity of symptoms and the individual's reproductive goals. Mild cases of adenomyosis may not require active treatment, and symptoms may improve after menopause. However, for women experiencing significant discomfort, various treatment options are available.
Hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills or progesterone-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs), are commonly recommended as a first-line therapy. These hormonal treatments can help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce heavy bleeding, and alleviate pain associated with adenomyosis. Another non-hormonal medication called tranexamic acid can be prescribed to reduce heavy bleeding during periods.
In cases where hormonal treatments are ineffective or not suitable, surgical interventions may be necessary. A hysterectomy, the surgical removal of the uterus, is considered a definitive treatment for adenomyosis. This procedure eliminates the source of the condition and provides long-term relief from symptoms. However, a hysterectomy is a major surgery and should be carefully considered, particularly for women who wish to preserve their fertility. Other surgical options, such as endometrial ablation, can be performed to remove or destroy the uterine lining, but these procedures may not fully address the underlying problem of adenomyosis.
Adenomyosis and Fertility
The impact of adenomyosis on fertility is still not fully understood. Some studies suggest that adenomyosis may decrease fertility, especially in women undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatments. However, the exact relationship between adenomyosis and fertility is complex, and many women with adenomyosis are still able to conceive naturally. If you are concerned about your fertility and have been diagnosed with adenomyosis, it is important to consult with a reproductive specialist who can provide personalized guidance.
Living with Adenomyosis
If you have been diagnosed with adenomyosis, there are steps you can take to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Using heat pads or hot water bottles on the abdomen can help alleviate pelvic pain. Over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen may provide temporary relief from cramping. It is also essential to maintain open communication with your healthcare provider to discuss any changes in your symptoms or treatment options.
Conclusion
Adenomyosis is a condition that can significantly impact a woman's reproductive health and quality of life. While the exact cause remains unknown, there are effective treatment options available. If you experience symptoms such as heavy bleeding, severe cramping, or chronic pelvic pain, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With the right management approach, women with adenomyosis can find relief from their symptoms and regain control over their reproductive health.