Table of Contents
- What is a Skin Rash?
- Types of Skin Rashes
- Contact Dermatitis
- Eczema
- Hives
- Psoriasis
- Viral Rashes
- Common Causes of Skin Rashes
- Symptoms of Skin Rashes
- Diagnosing Skin Rashes
- Physical Examination
- Biopsy and Allergy Tests
- Blood Tests
- Treating Skin Rashes
- Allergy Medications
- Anti-inflammatory Creams
- Immunosuppressants
- Oatmeal Baths
- Steroids
- Topical Immunomodulators
- Preventing Skin Rashes
- Complications of Skin Rashes
- When to Seek Medical Attention
- Living with Skin Rashes
1. What is a Skin Rash?
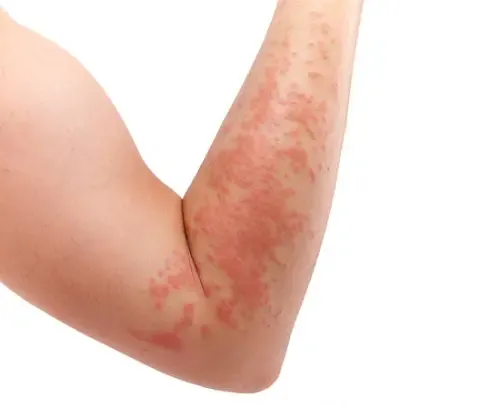
A skin rash is a condition characterized by red, inflamed, and bumpy skin. It can manifest in various forms, such as dry patches, blisters, hives, or scaly rashes. Skin rashes can be itchy, painful, or both, causing discomfort and affecting the quality of life. They can occur on any part of the body and vary in severity depending on the underlying cause.
2. Types of Skin Rashes
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a common type of skin rash caused by direct contact with an irritant or allergen. It occurs when the skin reacts negatively to substances like beauty products, soaps, detergents, chemicals, or plants such as poison ivy. The resulting rash is often itchy, red, and inflamed.
Eczema
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed patches. It commonly appears in childhood and may improve over time. People with eczema often have a family history of allergies or asthma.
Hives
Hives, or urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin. They can be caused by allergic reactions to allergens, insect stings, extreme temperature changes, or certain bacterial infections. Hives can appear and disappear rapidly, making them unpredictable and uncomfortable.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that leads to the rapid buildup of skin cells. This results in thick, scaly patches of skin that are often red and itchy. Psoriasis commonly affects the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, and genitals.
Viral Rashes
Skin rashes can also be caused by viral infections such as chickenpox, measles, and molluscum contagiosum. These rashes are often accompanied by other symptoms related to the specific viral illness.
3. Common Causes of Skin Rashes
Skin rashes can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Allergens in the environment, such as pollen, dust mites, or animal dander.
- Bacterial infections, such as strep throat, which can lead to conditions like scarlet fever.
- Skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or rosacea.
- Irritants like soaps, detergents, chemicals, or certain fabrics.
- Viral infections, including chickenpox, measles, or fifth disease.
Identifying the underlying cause of a skin rash is crucial for effective treatment and management.
4. Symptoms of Skin Rashes
The symptoms of a skin rash can vary depending on the type and cause. Common symptoms include:
- Dry or scaly skin.
- Blistering or raised bumps.
- Redness or inflammation.
- Itchiness or a burning sensation.
- Pain or tenderness.
- Spreading of the rash to other areas.
The severity and duration of these symptoms can vary, and some rashes may come and go periodically.
5. Diagnosing Skin Rashes
Diagnosing a skin rash involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and sometimes additional tests. Here are the common diagnostic methods used by healthcare providers:
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider will visually assess the rash, noting its appearance, location, and any associated symptoms. They may also inquire about the patient's medical history, previous exposure to irritants or allergens, and any recent changes in lifestyle or environment.
Biopsy and Allergy Tests
In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to determine the cause of a skin rash. A small sample of skin or tissue is taken for laboratory analysis to identify any viral or bacterial presence. Allergy tests, such as skin prick tests or patch tests, can help identify specific allergens that may be triggering the rash.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be conducted to check for antibodies or detect systemic illnesses that could be causing the skin rash. These tests can provide valuable insights into the overall health and immune response of the individual.
6. Treating Skin Rashes
The treatment of a skin rash depends on its underlying cause. While some rashes may resolve on their own, others may require medical intervention. Here are some common treatment options:
Allergy Medications
Oral antihistamines are often prescribed to reduce itching associated with skin rashes caused by allergies. These medications help alleviate discomfort and minimize the urge to scratch, which can worsen the rash.
Anti-inflammatory Creams
Topical corticosteroid creams, such as hydrocortisone, are commonly used to reduce inflammation and itching. These creams can provide temporary relief and promote healing of the affected skin.
Immunosuppressants
For rashes caused by immune system responses, such as eczema, immunosuppressant medications may be prescribed. These medications help calm the immune system and minimize inflammation, providing long-term relief.
Oatmeal Baths
Taking a warm bath with colloidal oatmeal can soothe dry, itchy skin rashes. Colloidal oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties and can provide temporary relief from discomfort.
Steroids
In more severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe a topical steroid cream or an oral steroid, such as prednisone. Steroids help reduce inflammation and alleviate itching, promoting faster healing of the rash.
Topical Immunomodulators
Topical immunomodulator medications, such as tacrolimus ointment and pimecrolimus cream, are used to modify the immune system's response to allergens. These prescription medications are effective in managing allergic contact dermatitis and reducing symptoms.
7. Preventing Skin Rashes
While not all skin rashes can be prevented, there are steps you can take to minimize the risk and reduce their occurrence. Here are some preventive measures:
- Avoid known triggers, such as allergens or irritants that have caused rashes in the past.
- Use mild, fragrance-free, and hypoallergenic soaps, cleansers, and moisturizers.
- Wash hands immediately after coming into contact with potential allergens or irritants.
- Practice good hygiene and keep the skin clean and dry.
- Avoid sharing personal items or clothing with individuals who have contagious viral rashes.
8. Complications of Skin Rashes
In most cases, skin rashes are not serious and resolve with appropriate treatment. However, complications can arise if the rash is not properly managed or if the skin becomes infected due to scratching. It is important to be aware of the following potential complications:
Anaphylaxis
Severe allergic reactions can lead to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening condition characterized by extreme swelling and closure of the air passages. Immediate medical attention, including the use of epinephrine, is necessary to counteract this allergic response.
Infection
Scratching an itchy rash can break the skin, making it susceptible to bacterial infections. Prompt treatment with antibiotics may be necessary to prevent further complications.
9. When to Seek Medical Attention
While many skin rashes can be managed at home, there are instances when medical attention is required. Contact your healthcare provider if:
- The rash is accompanied by severe trouble breathing or other signs of anaphylaxis.
- The rash appears suddenly and spreads rapidly.
- The rash covers a large area of the body or persists for an extended period.
- The rash is accompanied by a fever or other systemic symptoms.
- The rash blisters, forms open sores, or looks infected.
It is important to seek professional medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
10. Living with Skin Rashes
Living with skin rashes can be challenging, but it is possible to manage and alleviate symptoms effectively. By working closely with healthcare providers, following recommended treatment plans, and making lifestyle adjustments, individuals with skin rashes can improve their quality of life. Regular follow-up appointments and open communication with healthcare providers are essential for ongoing management and support.
In conclusion, skin rashes are a common dermatological issue that can significantly impact well-being. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can effectively manage their skin rashes and find relief from discomfort. If you are experiencing a skin rash, consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.